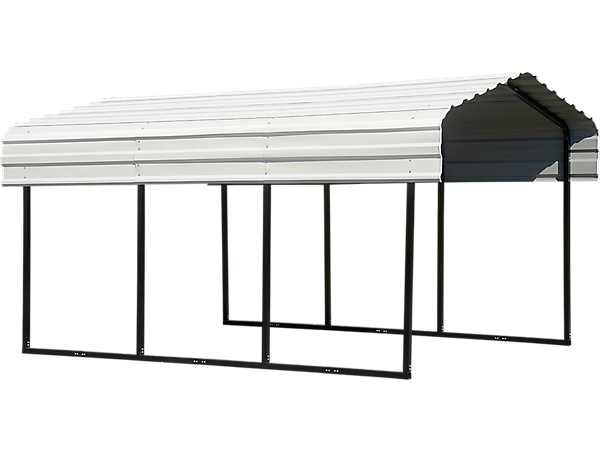
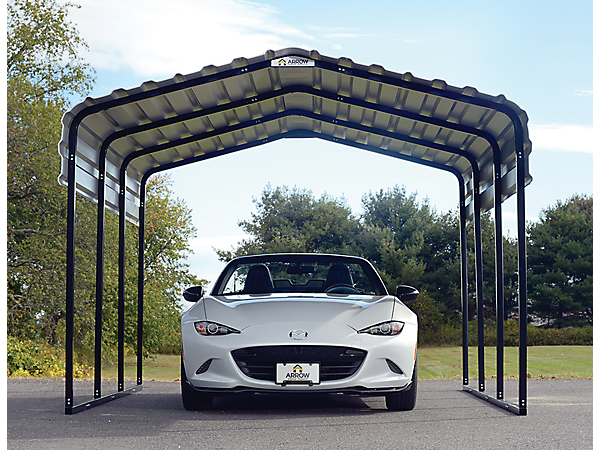
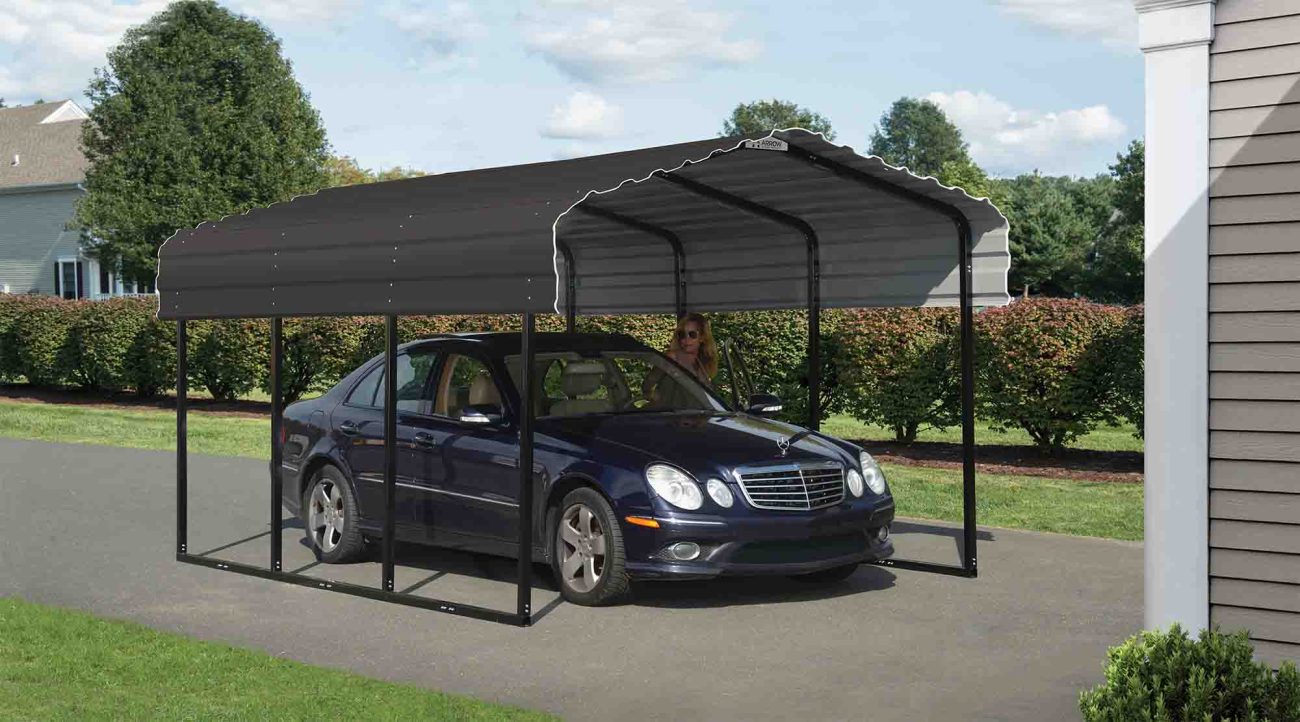
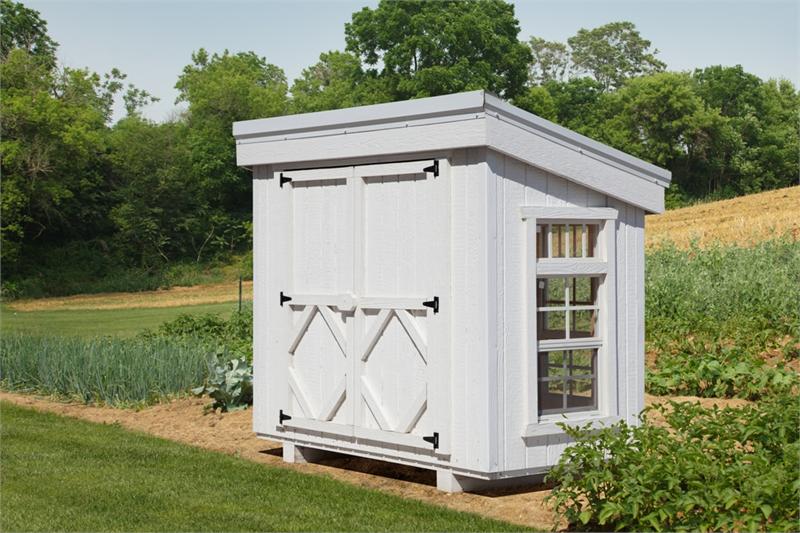
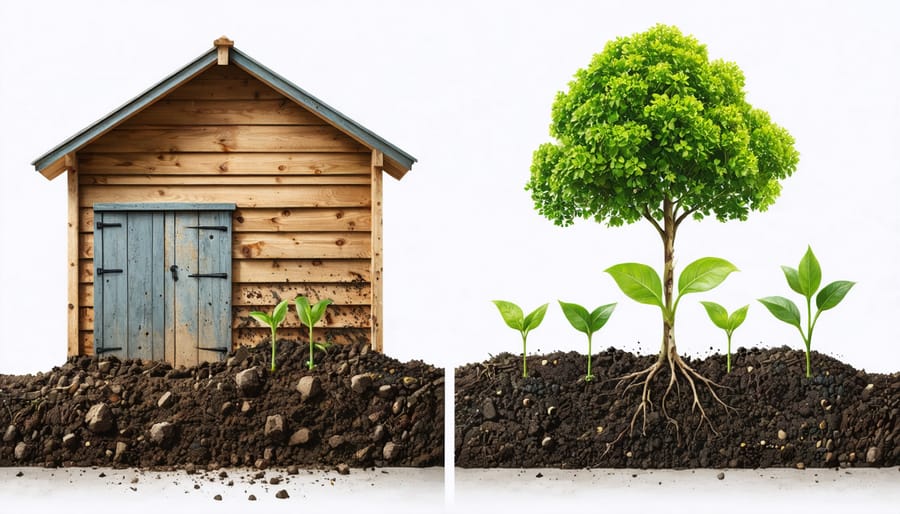
Parturient ut id tellus vulputatre ac ultrlices a part ouriesnt sapien dignissim partu rient a a inter drum vehicula. Ornare metus laoreet tincidunt eros rolem tristique pretium malada.
Cras rhoncus vivamus luctus platea arcu laoreet selm. Curae est condenectus sed hac a parturient vestibulum.