Transform your backyard into a year-round growing paradise with a four-season greenhouse that defies winter’s chill and summer’s scorching heat. Before planning your greenhouse, understand that successful four-season operation demands careful consideration of insulation, ventilation, and thermal mass storage. Modern greenhouse designs incorporate double-walled polycarbonate panels, automated temperature control systems, and ground-to-air heat transfer pipes to maintain optimal growing conditions throughout extreme weather changes. Whether you’re growing fresh vegetables in December or starting seedlings in February, a properly designed four-season greenhouse extends your growing calendar to 365 days, providing fresh produce and gardening joy no matter the weather outside. This guide walks you through essential design elements, material selection, and construction techniques that ensure your greenhouse performs efficiently across all seasons.
Essential Design Features for Year-Round Growing
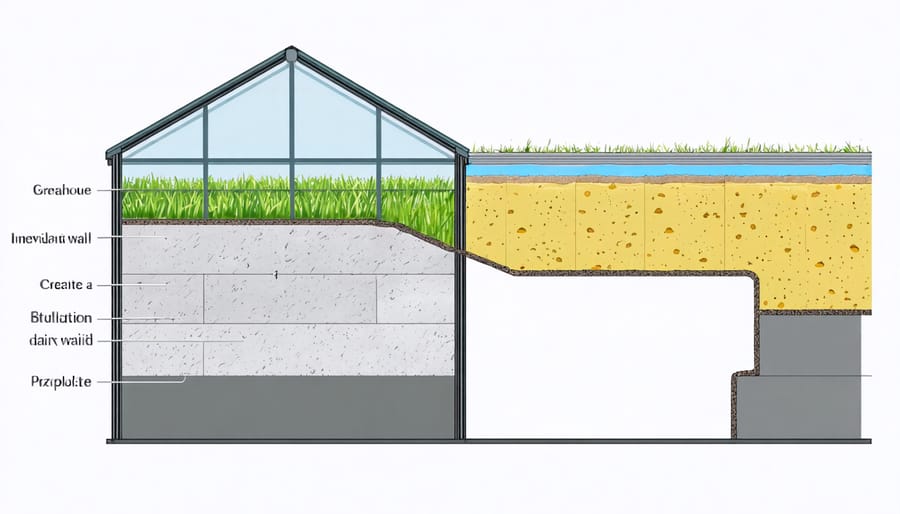
Insulation Requirements
Proper insulation is crucial for maintaining stable temperatures in your four-season greenhouse. Start with a double-wall polycarbonate panel system, which creates an insulating air gap while allowing maximum light transmission. For the foundation, use rigid foam insulation boards with an R-value of at least R-10 beneath the perimeter and extending 24 inches into the ground.
Consider installing bubble wrap insulation on the north wall, which receives minimal sunlight. This affordable solution adds an extra layer of protection without significantly reducing light. For gaps and seams, use weatherstripping tape and silicone caulk to prevent heat loss and drafts.
Ground-level insulation can be enhanced by creating a thermal mass system. Line the floor with gravel and incorporate water barrels painted black to absorb heat during the day and release it at night. During extreme weather, temporary insulation blankets can be draped over sensitive plants and along walls for additional protection.
Remember to insulate any water pipes running through your greenhouse to prevent freezing, using foam pipe insulation sleeves or heat tape for critical areas.
Ventilation Systems
A well-designed ventilation system is crucial for maintaining ideal growing conditions in your four-season greenhouse. Automated options include thermostat-controlled exhaust fans and solar-powered vent openers, which adjust based on temperature changes without requiring your presence. These systems typically activate when temperatures rise above 80°F, preventing plant stress and maintaining optimal growing conditions.
Manual ventilation features should include roll-up side panels and roof vents that you can adjust as needed. Position these vents strategically – lower vents on the windward side and upper vents on the opposite side – to create effective cross-ventilation. This natural airflow helps control humidity and strengthens plant stems.
For winter operation, consider installing a combination of passive and active systems. A solar-powered circulation fan keeps air moving on cold days without significantly impacting your energy bills. Adding adjustable intake vents near ground level helps manage humidity while maintaining necessary warmth. Remember to check your ventilation systems seasonally and keep moving parts well-maintained for reliable performance year-round.
Optimal Foundation and Structure
Foundation Types
Before you begin construction, it’s essential to prepare your greenhouse site with a solid foundation that can withstand year-round use. The most popular foundation options for four-season greenhouses include concrete slabs, concrete pier foundations, and gravel beds.
Concrete slabs offer superior stability and excellent insulation properties, making them ideal for cold climates. They provide a level surface for your greenhouse and help maintain consistent temperatures throughout the year. While more expensive initially, concrete slabs typically require minimal maintenance and last for decades.
Concrete pier foundations combine affordability with durability. These foundations elevate your greenhouse slightly off the ground, promoting better airflow and drainage. They’re particularly suitable for sloped terrain and areas with poor soil conditions. Installation is straightforward, making them a favorite among DIY enthusiasts.
Gravel bed foundations are the most budget-friendly option and offer excellent drainage capabilities. A properly installed gravel foundation consists of multiple layers, including landscape fabric, coarse gravel, and finer gravel on top. While they may require occasional releveling, gravel beds are easily customizable and can be enhanced with additional insulation materials for better temperature control.
Consider your local climate, budget, and soil conditions when selecting your foundation type. Each option has its merits, but the key is ensuring proper installation for long-term greenhouse stability.

Frame Materials
When building a four-season greenhouse, choosing the right frame material is crucial for long-term durability and weather resistance. The most popular options include aluminum, galvanized steel, and treated wood, each offering unique benefits for year-round growing.
Aluminum frames are naturally rust-resistant and lightweight, making them ideal for DIY installation. While initially more expensive, they require minimal maintenance and can last decades with proper care. Many gardeners prefer aluminum for its clean appearance and ability to reflect light back onto plants.
For maximum strength and stability, metal frame construction using galvanized steel is hard to beat. These frames can handle heavy snow loads and strong winds, making them perfect for regions with extreme weather conditions. The galvanized coating prevents rust and corrosion, ensuring your greenhouse remains sturdy year after year.
Treated wood frames offer a traditional, natural look and excellent insulation properties. Cedar and pressure-treated pine are popular choices due to their natural resistance to decay and insects. However, wood frames require more maintenance and may need periodic sealing or replacement of damaged sections.
When selecting your frame material, consider your local climate, budget, and maintenance preferences. For areas with heavy snowfall or strong winds, opt for stronger materials like galvanized steel. If you’re in a milder climate, aluminum or wood frames might better suit your needs while providing adequate protection for your plants.
Climate Control Solutions

Winter Heating Options
Maintaining consistent warmth in your greenhouse during winter is crucial for year-round growing success. Several effective heating options can help you achieve optimal temperatures, even during the coldest months.
Electric heaters are popular for their convenience and precise temperature control. Fan-forced models provide excellent heat distribution and can be connected to thermostats for automatic operation. While they’re effective, consider their impact on energy bills during peak winter months.
Passive solar heating systems work wonderfully when properly implemented. Dark-colored thermal mass materials, like water barrels or stone floors, absorb heat during the day and release it at night. This method is cost-effective but may need backup heating in extremely cold regions.
Propane heaters offer powerful heating capabilities and work independently of electricity. They’re especially useful in areas prone to power outages. However, ensure proper ventilation and carbon monoxide monitoring when using these units.
For smaller greenhouses, heat mats or soil cables can provide targeted warmth to plant roots. Combined with good insulation methods like bubble wrap on walls and thermal curtains, these solutions help maintain consistent temperatures while being energy-efficient.
Consider implementing multiple heating methods for redundancy and optimal temperature control. Remember to monitor humidity levels, as winter heating can sometimes create overly dry conditions that affect plant health.
Summer Cooling Strategies
Keeping your greenhouse cool during summer months is crucial for maintaining healthy plants and comfortable working conditions. Start by installing adjustable roof vents, which allow hot air to escape naturally through convection. Complement these with roll-up side panels or louvered windows that create essential cross-ventilation when opened.
Shade cloth is your best friend during peak summer heat – opt for a 30-50% shade rating for most plants. Install it on the exterior of your greenhouse to block intense sunlight before it enters and creates a greenhouse effect. Many gardeners use retractable systems that can be adjusted based on daily conditions.
An automated ventilation system with thermostat-controlled fans takes the guesswork out of temperature management. Position intake fans low on one end and exhaust fans high on the opposite end to create optimal air flow. For added cooling, consider installing a misting system that can reduce temperatures by up to 10-15 degrees through evaporative cooling.
Don’t overlook simple solutions like painting your greenhouse with whitewash during summer months or installing bubble wrap insulation with the bubbles facing outward to reflect heat. Keep your plants elevated on benches to improve air circulation, and consider using light-colored ground cover to minimize heat absorption from the floor.
Remember to monitor temperature regularly and adjust your cooling strategies as needed throughout the season. A combination of these methods will help maintain ideal growing conditions even during the hottest days.
Seasonal Maintenance Schedule
Seasonal Checklist
Keeping your four-season greenhouse in top condition requires regular maintenance throughout the year. Here’s your essential seasonal checklist to ensure your greenhouse thrives year-round:
Spring (March-May):
– Clean and sanitize all surfaces thoroughly
– Check and repair any winter damage to structure
– Install shade cloth for increasing sunlight
– Test and repair irrigation systems
– Start seedlings and prepare growing beds
– Clean and test ventilation fans
– Check seals around doors and vents
Summer (June-August):
– Monitor and adjust ventilation daily
– Water plants early morning or evening
– Maintain consistent humidity levels
– Prune and maintain plants regularly
– Check for pest infestations weekly
– Clean fans and vents monthly
– Ensure shade cloth is properly positioned
Fall (September-November):
– Remove shade cloth
– Clean and store summer equipment
– Check heating system functionality
– Seal any drafts or leaks
– Clear gutters and drainage systems
– Inspect greenhouse frame for repairs
– Clean and sterilize growing areas
Winter (December-February):
– Monitor heating system daily
– Remove snow from roof promptly
– Check insulation effectiveness
– Maintain minimum temperature requirements
– Clean condensation regularly
– Protect plants from cold spots
– Monitor humidity levels carefully
Remember to keep detailed records of maintenance tasks and any issues that arise. This helps track patterns and prevent future problems while ensuring your greenhouse remains productive throughout all four seasons.
Common Issues and Solutions
Even the best-planned four-season greenhouses can face challenges throughout the year. In winter, inadequate insulation might lead to heat loss and high energy costs. Combat this by adding a second layer of greenhouse plastic or installing thermal curtains. Temperature fluctuations between day and night can stress plants – using thermal mass solutions like water barrels or stone pathways helps maintain stable temperatures.
During summer, overheating is a common issue. Install proper ventilation systems and consider adding shade cloth to reduce intense sunlight. Humidity control can be tricky in spring and fall; combat excess moisture with good air circulation and avoiding overwatering. If condensation becomes problematic, install fans and ensure proper spacing between plants.
Foundation settling might occur over time, causing structural issues. Regular maintenance checks and immediate repairs of any cracks or gaps will prevent bigger problems. Pest invasions can happen year-round – implement physical barriers and maintain a clean environment. For areas with heavy snow loads, ensure your greenhouse design includes adequate roof pitch and strong support beams to prevent collapse.
Building a four-season greenhouse is an exciting journey that can transform your gardening experience and provide fresh produce year-round. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the essential elements needed to create a successful greenhouse that works in every season – from proper insulation and ventilation to heating systems and crop planning.
Remember that the key to success lies in careful planning and attention to detail. By incorporating the right materials, maintaining proper temperature control, and implementing effective growing strategies, you can create a thriving greenhouse environment regardless of the weather outside.
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting, building a four-season greenhouse is a rewarding project that pays dividends throughout the year. The initial investment in time and resources will be well worth the satisfaction of harvesting fresh vegetables in winter or starting your spring seedlings early.
Don’t be intimidated by the process – take it one step at a time. Start with a solid foundation, both literally and figuratively, by carefully considering your location and layout. Then work systematically through the construction process, paying special attention to insulation and climate control features.
Ready to begin your greenhouse journey? With these plans and guidelines in hand, you’re well-equipped to create a productive growing space that serves you through all four seasons. Happy building, and here’s to years of successful greenhouse gardening ahead!





Leave a Reply