Power outages can strike without warning, leaving homes vulnerable and families unprepared. Installing a reliable emergency power supply isn’t just about convenience—it’s about maintaining essential services and protecting your family during critical situations. Whether you’re facing severe weather events, grid failures, or unexpected blackouts, a well-planned shed electrification basics and backup power system ensures your home remains functional when you need it most.
Modern homes rely heavily on electricity for heating, cooling, refrigeration, and medical equipment. A comprehensive emergency power solution transforms uncertainty into preparedness, providing peace of mind and practical protection against power-related emergencies. From portable generators to sophisticated whole-house backup systems, today’s homeowners have multiple options to match their specific needs and budget constraints.
Understanding your power requirements, selecting the right equipment, and maintaining your backup system are crucial steps in creating a reliable emergency power solution. This guide will help you navigate the essential considerations for keeping your home powered when the grid goes down.
Why Your Shed Needs Emergency Power
Protecting Valuable Equipment
When setting up your emergency power supply, protecting your valuable equipment should be a top priority. Start by creating an inventory of essential items that need protection, including computers, refrigerators, and sensitive electronics. Install surge protectors between your backup power source and connected devices to guard against sudden voltage spikes that could damage your equipment.
For temperature-sensitive items like medications or food storage, consider dedicated battery backup systems for refrigerators and freezers. Keep these units on separate circuits to ensure they receive consistent power without competing with other appliances.
Power tools require special attention during emergency situations. Store them in a dry location and use voltage regulators when connecting to backup power sources. This helps maintain stable power delivery and prevents damage from fluctuating current.
Consider using uninterruptible power supply (UPS) units for computers and other sensitive electronics. These devices provide instantaneous backup power and help smooth out power irregularities that could harm your equipment. Remember to regularly test your protection systems and replace surge protectors every few years to maintain optimal performance.
Safety and Security Concerns
Safety should always be your top priority when setting up an emergency power supply for your home and outdoor structures. Proper shed lighting solutions and security systems need reliable backup power to function during outages. Install battery-powered motion sensors and emergency lights at key entry points and along pathways to maintain visibility and security.
Keep your backup power system in a well-ventilated area, away from moisture and extreme temperatures. If using a generator, never operate it indoors or in enclosed spaces due to carbon monoxide risks. Install carbon monoxide detectors near your power setup and ensure all family members know their locations.
Regularly test your emergency power system, including automatic transfer switches and backup batteries. Create a clear emergency plan that includes power-up procedures and safety protocols. Label all circuits and switches clearly, and keep a flashlight and basic tools nearby. Store fuel safely in approved containers away from living spaces, and maintain an updated list of emergency contacts.
Remember to check local regulations regarding backup power systems and obtain necessary permits before installation.

Best Backup Power Options for Your Shed
Portable Generators
Portable generators are a popular choice for home emergency power, offering flexibility and reliable backup when you need it most. These units come in various sizes, typically ranging from 2,000 to 10,000 watts, making them suitable for different household needs. Most homeowners find that a 5,000-7,500-watt generator provides adequate power for essential appliances like refrigerators, lighting, and basic electronics.
When selecting a portable generator, consider both running watts (continuous power needed) and starting watts (extra power required when appliances first turn on). For instance, while your refrigerator might need 700 watts to run, it could require up to 2,200 watts to start. Make a list of critical appliances you’ll need during an outage and add up their power requirements to determine the right size.
Modern portable generators offer various fuel options. Traditional gasoline models are common and readily available, while dual-fuel generators can run on both gasoline and propane, offering greater flexibility. Some premium models even feature tri-fuel capability, adding natural gas to the mix.
Installation considerations are crucial for safe operation. Always place your generator outdoors, at least 20 feet from your home, with the exhaust pointing away from windows and doors. A transfer switch or interlock device is essential for safely connecting the generator to your home’s electrical system – never plug directly into a wall outlet, as this can create dangerous backfeed.
Remember to perform regular maintenance: check oil levels, test the unit monthly, and store fuel properly with stabilizer added. Keep spare parts and maintenance supplies on hand, especially during storm seasons when you’re most likely to need backup power.
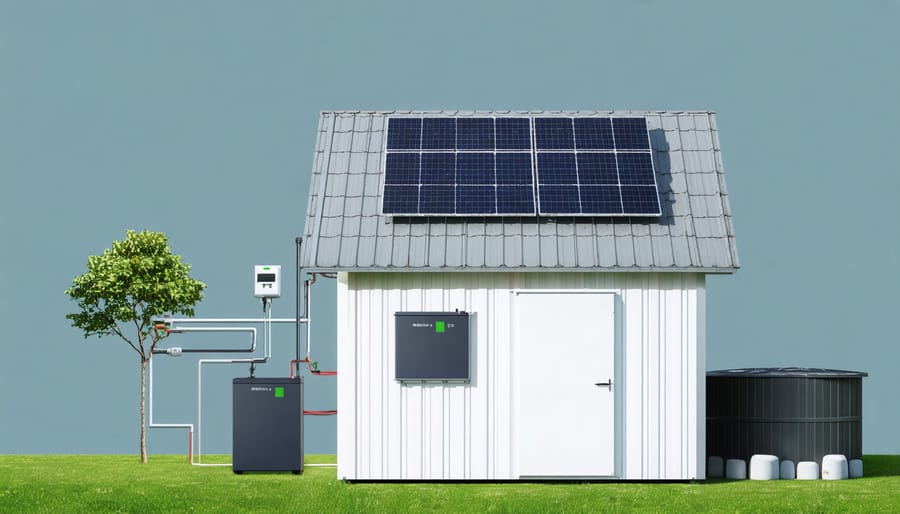
Solar Power Systems
Solar power systems offer a sustainable and environmentally friendly solution for your home’s emergency power needs. These systems typically consist of three main components: solar panels, a battery bank, and an inverter. When properly sized and installed, they can provide reliable backup power during outages while reducing your daily energy costs.
For optimal performance, start by determining your power requirements. Calculate the essential appliances and devices you’ll need to run during an outage, then add about 20% for safety margin. Most homeowners find that a 4-6 kW system with 8-12 solar panels provides sufficient backup power for basic needs.
The heart of your solar backup system is the battery bank, where excess energy is stored for use during nighttime or outages. Modern lithium-ion batteries are becoming increasingly popular due to their longer lifespan and compact size compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. For a typical home, a 10-14 kWh battery capacity usually provides enough storage for 24-48 hours of essential power.
Installing a solar power system requires careful planning and consideration. While DIY installation is possible for those with electrical experience, we recommend following our detailed solar power installation guide or consulting with certified professionals to ensure safety and optimal performance.
Remember to position your solar panels where they’ll receive maximum sunlight exposure, typically on south-facing roof sections with a 30-45 degree tilt. Regular maintenance is minimal but important – keep panels clean, check connections quarterly, and monitor battery health through your system’s management interface.
One often overlooked advantage of solar backup systems is their daily utility. Unlike generators that sit idle until an emergency, solar systems work year-round to reduce your energy bills while staying ready for power outages. Many homeowners report 50-80% reductions in their monthly electricity costs after installation, making this investment particularly attractive for long-term emergency preparedness.

Battery Backup Systems
Battery backup systems offer reliable emergency power solutions for your home, combining convenience with peace of mind. Deep cycle batteries stand out as workhorses in backup power, designed to provide steady power over extended periods. Unlike car batteries, these specialized units can handle repeated discharge and recharge cycles without damage, making them perfect for home backup situations.
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems serve as your first line of defense against power outages. These smart devices not only provide instant backup power but also protect your sensitive electronics from harmful power surges and fluctuations. For home office setups or medical equipment, a UPS can maintain power long enough to safely save work or switch to alternative power sources.
Power banks have evolved beyond just charging phones. Modern high-capacity power banks can run small appliances, CPAP machines, and even refrigerators for short periods. Many homeowners keep several sizes on hand – compact units for personal devices and larger stations for household needs. Look for models with multiple output options, including standard outlets, USB ports, and 12V connections.
When setting up your battery backup system, consider creating layers of protection. Start with UPS units for critical electronics, add power banks for portable needs, and install deep cycle batteries for longer-term backup. Regular maintenance is crucial – check connections monthly, test systems quarterly, and replace batteries according to manufacturer guidelines. Remember to store backup batteries in a cool, dry place and keep them charged, especially during storm seasons.
For maximum effectiveness, calculate your power needs beforehand and choose appropriately sized systems. Most families find that a combination of these backup solutions provides the most comprehensive emergency power coverage.
Installation and Safety Tips
Proper Wiring and Connections
Ensuring proper electrical wiring is crucial for your home’s emergency power supply system. Start by having a qualified electrician install a transfer switch, which prevents dangerous backfeeding and allows safe connection of your backup power source to your home’s electrical panel.
Always use the correct gauge wire for your system’s capacity – using undersized wiring can create fire hazards and reduce system efficiency. When connecting your backup power source, ensure all connections are weather-protected and properly insulated. Install surge protectors to safeguard sensitive electronics from power fluctuations.
Common mistakes to avoid include:
– Skipping the transfer switch installation
– Using indoor-rated cables for outdoor connections
– Overloading circuits with too many appliances
– Neglecting to ground the system properly
– Making connections without turning off the main power
Keep all wiring connections in waterproof junction boxes and label all circuits clearly for easy identification during emergencies. Regular inspection of wiring connections helps prevent loose terminals that could cause system failure when you need it most.
Remember to follow local electrical codes and obtain necessary permits before installation. While DIY installation might seem tempting, incorrect wiring can create serious safety hazards and potentially damage your home’s electrical system. When in doubt, always consult a licensed electrician to ensure your emergency power supply is installed safely and functions reliably when needed.
Maintenance and Testing
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure your emergency power supply works when you need it most. Start by creating a monthly testing schedule – mark it on your calendar and stick to it. During these checks, run your backup power system for at least 30 minutes to verify all components are functioning correctly.
For battery-based systems, check the electrolyte levels monthly if you have flooded lead-acid batteries. Clean the terminals and check for any signs of corrosion. Battery voltage should be tested under both no-load and load conditions to ensure proper charging and performance.
If you have a generator, run it monthly for about 20-30 minutes with a typical load. This prevents fuel from becoming stale and keeps internal components lubricated. Change the oil according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, typically every 50-100 hours of use or annually, whichever comes first.
Keep detailed maintenance logs recording dates, actions taken, and any issues found. This helps track patterns and predict when components might need replacement. Store spare parts like filters, fuses, and basic tools in an easily accessible location.
For solar systems, inspect panels quarterly for dirt, debris, or damage. Clean them gently with water and check all connections for tightness. Verify that charge controllers and inverters are functioning properly by checking their display readings.
Test all automatic transfer switches twice yearly to ensure they engage properly during power outages. Finally, review and update your emergency procedures annually, making sure all family members know how to safely operate the system.
Having a reliable home emergency power supply is essential for maintaining comfort and safety during unexpected outages. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored various options, from portable generators to comprehensive backup systems, each offering unique advantages for different household needs and budgets.
Remember that the best emergency power solution depends on your specific requirements, including power consumption, available space, and local regulations. Whether you choose a simple portable generator for basic needs or invest in a whole-house backup system, proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial for ensuring reliability when you need it most.
Key takeaways include conducting a thorough assessment of your power needs, considering both short-term and long-term costs, and prioritizing safety features. Don’t forget to maintain adequate fuel supplies, regularly test your system, and keep all documentation and operating instructions easily accessible.
For optimal preparation, we recommend creating a detailed emergency power plan that includes regular maintenance schedules, safety protocols, and clear instructions for family members. Consider starting with a smaller, portable solution and upgrading as needed based on your experience and requirements.
Remember, the goal isn’t just to have backup power – it’s to ensure your family’s comfort and safety during emergencies while protecting your home’s essential systems and valuable appliances.





Leave a Reply