Essential Landscape Safety Rules That Could Save Your Life
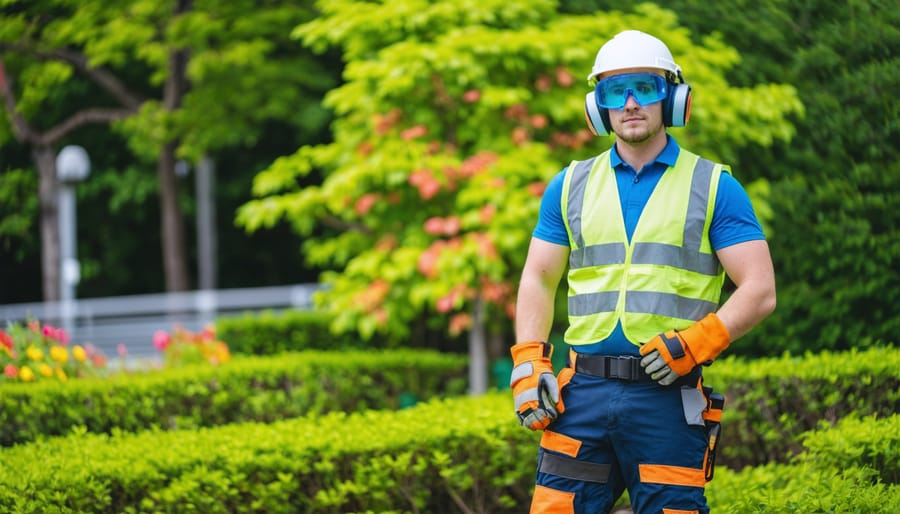

Safeguard your landscape work environment with a comprehensive safety protocol that protects both workers and property. From operating heavy machinery to handling chemical treatments, landscape maintenance demands strict adherence to safety guidelines that prevent accidents and ensure regulatory compliance. This essential manual establishes fundamental practices for personal protective equipment (PPE), equipment operation, weather considerations, and emergency response procedures.
Professional landscaping teams and property owners must prioritize safety through proper training, regular equipment inspections, and clear communication protocols. Whether managing a small residential garden or maintaining extensive commercial grounds, understanding and implementing these safety measures prevents workplace injuries, reduces liability risks, and promotes efficient operation.
This landscape safety manual provides systematic guidance for creating a secure work environment, incorporating industry best practices and OSHA requirements. Learn critical procedures for hazard identification, proper tool handling, and emergency preparedness while maintaining the natural beauty of outdoor spaces.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Requirements
Essential Safety Gear Checklist
Before starting any landscaping work, ensure you have these essential safety items ready:
Safety Glasses: Always wear impact-resistant glasses to protect your eyes from flying debris, dust, and chemical splashes. Choose pairs with side shields for maximum protection.
Work Gloves: Use heavy-duty gloves appropriate for your task – leather for handling tools and thorny plants, rubber for chemical applications, and grip-enhanced gloves for wet conditions.
Steel-Toed Boots: Protect your feet with slip-resistant, waterproof boots featuring steel toes to guard against falling objects and sharp tools.
Hearing Protection: Use earplugs or earmuffs when operating loud equipment like mowers or leaf blowers. Double up on protection for especially noisy machinery.
High-Visibility Clothing: Wear bright, reflective gear, especially when working near roads or in low-light conditions. Choose breathable materials for comfort.
Sun Protection: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen, wear a wide-brimmed hat, and use UV-protective sunglasses for outdoor work.
Dust Mask/Respirator: Use appropriate respiratory protection when handling chemicals, mulch, or creating dust. Ensure proper fit for maximum effectiveness.
First Aid Kit: Keep a well-stocked kit nearby containing bandages, antiseptic wipes, gauze, and basic medical supplies for emergency response.

Weather-Specific Protection
Weather conditions can significantly impact landscape work safety, requiring specific precautions and weather protection solutions for different situations. During hot weather, schedule intensive tasks for cooler morning hours, take frequent breaks in shaded areas, and maintain proper hydration. Always keep sunscreen, protective clothing, and cooling towels readily available.
For cold weather operations, layer clothing appropriately and wear insulated, water-resistant gear. Watch for signs of hypothermia and frostbite, particularly when working with wet materials or in freezing conditions. Keep emergency warming supplies in your work area.
During wet conditions, use non-slip footwear and ensure proper drainage in work zones. Avoid operating electrical equipment in rain and cover power tools when not in use. For windy conditions, secure loose materials and wear eye protection to guard against airborne debris.
Monitor weather forecasts regularly and adjust work schedules accordingly. When thunder is heard, immediately cease outdoor activities and seek appropriate shelter. Remember that no landscape task is worth risking personal safety in severe weather conditions.
Equipment and Tool Safety Protocols
Power Tool Safety Guidelines
Operating power tools safely requires strict adherence to fundamental guidelines. Always start by ensuring proper workspace lighting and maintaining a clear, debris-free work area. Before starting any power tool, inspect it thoroughly for damaged parts, loose connections, or frayed cords.
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses, ear protection, and work gloves. Avoid loose clothing, jewelry, or anything that could get caught in moving parts. Keep both hands on tools designed for two-handed operation, and never remove or modify safety guards.
For gas-powered equipment, fuel up outdoors and only when the engine is cool. Electric tools should be unplugged when not in use and during maintenance. Never use electric tools in wet conditions or with damaged cords.
Maintain proper stance and balance while operating power tools. Keep bystanders at a safe distance, and never work when tired or under the influence of medications that cause drowsiness. Store tools in a dry, secure location out of children’s reach.
Remember to clean and maintain your tools regularly according to manufacturer specifications. Dull or poorly maintained tools can be dangerous and less effective. If a tool malfunctions, discontinue use immediately and have it serviced by a qualified professional.
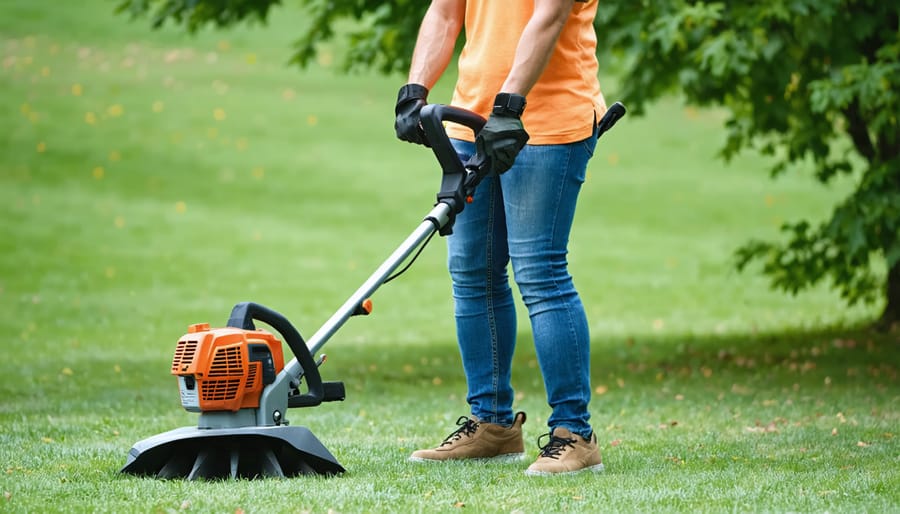

Manual Tool Safety Best Practices
Proper handling of manual tools is essential for safe and effective landscaping work. Always inspect your tools before use, checking for loose handles, rust, or damage that could compromise safety. Keep tools sharp and well-maintained, as dull equipment requires more force and increases accident risk.
When using hand tools, maintain a firm grip and proper stance with feet shoulder-width apart. Avoid overreaching or working in awkward positions that could strain your body or cause loss of balance. Keep your workspace clear of obstacles and ensure adequate lighting for visibility.
Store tools properly when not in use, keeping sharp edges covered and tools organized in a designated area. Never leave tools lying on the ground where they could become tripping hazards. Clean tools after each use to prevent rust and maintain their effectiveness.
For digging tools like shovels and spades, wear sturdy boots and step on the blade with your full body weight rather than straining your back. When using pruning shears or loppers, keep your free hand away from the cutting area and maintain awareness of surrounding branches.
Remember to use tools only for their intended purpose – improvising with the wrong tool for a job often leads to accidents. Take regular breaks to prevent fatigue, which can impair judgment and increase the risk of injury. If a tool feels uncomfortable or unsafe to use, stop immediately and seek a more appropriate solution.
Environmental Hazard Assessment
Site Survey Procedures
Before starting any landscape work, conducting a thorough site survey is essential for everyone’s safety. Begin by walking the entire work area to identify potential hazards such as uneven ground, hidden holes, or obstacles. Mark any underground utilities after contacting your local utility service for proper line identification.
Check the area for overhead power lines and ensure all equipment and tools will maintain a safe distance during operation. Assess the terrain’s slope and stability, particularly after rainfall, to prevent accidents from slips or equipment tipping. When working in warm conditions, identify shaded areas and plan for heat safety measures to protect your team.
Document any existing property damage or hazardous conditions with photos before beginning work. This helps protect both you and the property owner. Verify access points for emergency vehicles and establish a clear evacuation route. Set up temporary safety barriers or warning signs where needed to protect both workers and passersby.
Finally, brief all team members on identified hazards and safety protocols. Create a site-specific safety plan that includes emergency contact numbers and the locations of first-aid supplies. Remember to update your survey if site conditions change during the project.
Natural Hazard Management
When working in outdoor spaces, it’s crucial to be aware of and prepared for natural hazards. Start by conducting a thorough inspection of your workspace for signs of wildlife activity, such as nests or burrows. Keep your weather-resistant workspace materials properly stored to avoid attracting animals seeking shelter.
For insect protection, wear light-colored, long-sleeved clothing and apply EPA-approved insect repellent. Be especially vigilant during dawn and dusk when insects are most active. Keep a first-aid kit nearby that includes antihistamines for potential bee or wasp stings.
Learn to identify common poisonous plants in your area, such as poison ivy, oak, and sumac. Wear thick gloves and protective clothing when working near vegetation. If exposure occurs, wash the affected area immediately with soap and water, and seek medical attention if a severe reaction develops.
Maintain your landscape by regularly trimming overgrowth and removing debris that could harbor unwanted wildlife. Consider installing motion-sensor lights and securing garbage bins to discourage nocturnal creatures. If you encounter aggressive wildlife, back away slowly and contact local animal control for assistance.
Emergency Response Procedures
First Aid Essentials
Every landscape professional should maintain a well-stocked first aid kit and know basic emergency procedures. Keep your first aid kit readily accessible and check it monthly to replace expired items or replenish used supplies.
Essential items for your landscape first aid kit should include:
– Adhesive bandages in various sizes
– Sterile gauze pads and rolls
– Medical tape
– Antiseptic wipes and solution
– Antibiotic ointment
– Pain relief medication
– Scissors and tweezers
– Clean work gloves
– Eye wash solution
– Instant cold and heat packs
– Emergency contact information
For common landscape injuries, remember these basic procedures:
– For cuts and scrapes: Clean the wound with antiseptic, apply antibiotic ointment, and cover with an appropriate bandage
– For sprains: Apply ice, provide compression, and elevate the affected area
– For heat exhaustion: Move to a cool area, provide water, and apply cool compresses
– For insect stings: Remove the stinger if present, clean the area, and apply ice to reduce swelling
Always keep a charged cell phone nearby for emergency calls. Consider taking a basic first aid certification course to better prepare for workplace emergencies. For serious injuries, call emergency services immediately and keep the injured person stable until help arrives.
Emergency Communication Plan
Clear communication during emergencies can mean the difference between a minor incident and a serious situation. Every landscape team should establish and maintain an emergency communication plan that all workers know by heart. Keep a list of emergency contacts, including local emergency services, supervisors, and designated first aid responders, posted in visible locations and saved in workers’ phones.
When an accident occurs, follow these steps:
1. Assess the situation quickly and ensure the area is safe
2. Call 911 immediately if there are serious injuries
3. Alert the designated site supervisor
4. Provide first aid if you’re trained and it’s safe to do so
5. Keep other workers away from any hazardous areas
Each work vehicle should contain a waterproof emergency contact card with:
– Emergency service numbers
– Nearest hospital locations
– Supervisor contact information
– Company address and GPS coordinates
– Utility emergency numbers
Regular emergency response drills help teams stay prepared. Practice scenarios should include common landscaping emergencies like equipment accidents, heat exhaustion, or chemical exposure. Document all incidents, no matter how minor, using standardized reporting forms.
Remember to update emergency contact information quarterly and whenever staff changes occur. Having a clear chain of command during emergencies prevents confusion and ensures swift, appropriate responses to any situation.
Maintaining a safe landscape environment is not just about following rules—it’s about protecting yourself, your team, and your property. Throughout this manual, we’ve covered essential safety protocols that form the foundation of responsible landscaping practices. Remember that proper protective equipment, from safety glasses to steel-toed boots, is your first line of defense against potential injuries.
Regular equipment maintenance and inspection aren’t just recommendations—they’re crucial steps that prevent accidents and extend the life of your tools. Always conduct thorough checks before starting any landscaping task, and never bypass safety features or take shortcuts that could compromise your well-being.
Weather awareness and proper planning remain vital components of landscape safety. Check forecasts before beginning outdoor work and adjust your schedule accordingly. Keep emergency contact numbers readily available, and ensure all workers know the location of first-aid supplies and emergency procedures.
Most importantly, create and maintain a culture of safety in your landscaping activities. Whether you’re a homeowner maintaining your yard or a professional landscaper, these safety guidelines protect everyone involved. Take time to train new workers properly, refresh safety knowledge regularly, and always report hazardous conditions immediately.
By following these safety protocols consistently, you’ll create a safer, more efficient working environment while achieving beautiful landscape results. Remember, no landscape project is worth compromising safety—when in doubt, always err on the side of caution.

