Transform Your Home with an All-Season Greenhouse Extension
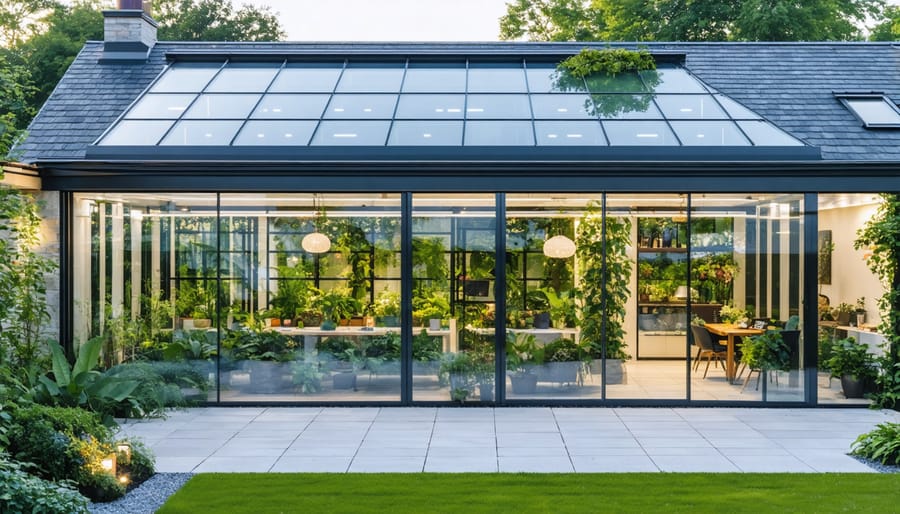

Transform your home into a year-round growing paradise by attaching a four-season greenhouse construction to your existing structure. This smart addition not only extends your growing season but also reduces heating costs by sharing your home’s thermal mass and existing utilities. Modern attached greenhouses integrate seamlessly with your home’s architecture while creating a controlled environment for vegetables, herbs, and tropical plants throughout all seasons. By connecting directly to your living space, these structures offer convenient access to fresh produce and create a stunning transitional area that doubles as a sunroom or relaxation space. The combination of proper insulation, ventilation systems, and strategic placement against your home’s southern exposure enables year-round cultivation regardless of external weather conditions. Whether you’re an avid gardener or simply seeking to enhance your home’s sustainability, an attached greenhouse represents a practical investment in both property value and self-sufficiency.\n\n\n
 \n
\n\n\n
Benefits of Attaching a Greenhouse to Your Home
\n\n
Energy Efficiency and Heat Transfer
\n\nAn attached greenhouse can significantly improve your home’s energy efficiency by acting as a natural temperature buffer. During winter months, the greenhouse captures solar heat, which can help warm adjacent rooms and reduce heating costs. Many homeowners report saving up to 15-20% on their winter heating bills after adding an attached greenhouse.\n\nIn summer, proper ventilation systems allow the greenhouse to assist in home cooling. By implementing shade cloths and automatic vents, you can create cooling air circulation patterns that benefit both the greenhouse and your home. The greenhouse’s thermal mass – typically concrete floors or water barrels – stores heat during the day and releases it slowly at night, helping maintain consistent temperatures.\n\nThe connection point between your home and greenhouse is crucial for optimal heat transfer. Installing a thermal door or multiple sliding doors lets you control the air exchange between spaces. Some gardeners use fans to actively circulate warm greenhouse air into their homes during sunny winter days, maximizing the energy-saving benefits of their attached greenhouse while maintaining comfortable growing conditions for their plants.\n\n
Year-Round Growing Potential
\n\nA greenhouse attached to your home opens up incredible possibilities for year-round growing techniques, transforming your gardening experience across all seasons. In winter, while outdoor gardens lie dormant, your attached greenhouse maintains comfortable temperatures for growing hearty greens, herbs, and cold-tolerant vegetables. Spring brings optimal conditions for starting seedlings and nurturing early crops, giving you a head start on the growing season.\n\nSummer’s abundance continues in your climate-controlled space, where you can grow heat-loving plants like tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers with protection from harsh elements. The controlled environment also allows for extending the fall growing season well into winter, making it possible to harvest fresh produce even as temperatures drop outside.\n\nWith proper temperature regulation and climate control, you can maintain a continuous cycle of planting and harvesting throughout the year. This means fresh herbs for cooking, homegrown vegetables for your table, and the joy of gardening regardless of outdoor conditions. The attached greenhouse truly becomes a living extension of your home, providing both functionality and year-round growing pleasure.\n\n\n
Design Considerations and Planning
\n\n
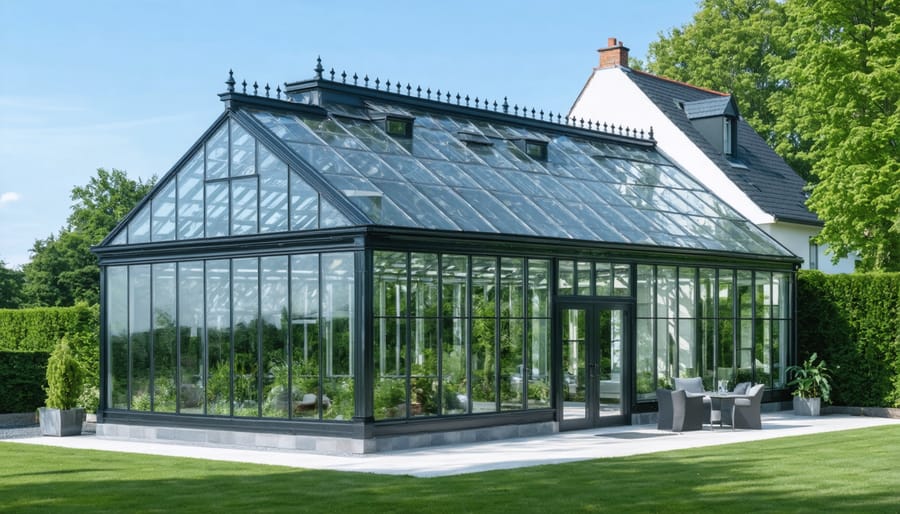
Location and Orientation
\n\nWhen considering greenhouse planning considerations, proper location and orientation are crucial for maximizing your attached greenhouse’s year-round performance. The ideal placement is on the south-facing side of your home, where it will receive the most direct sunlight throughout the day. This orientation helps maintain optimal growing conditions and reduces heating costs during colder months.\n\nEast or west-facing locations can work but may require additional climate control measures. Avoid north-facing positions, as they receive minimal direct sunlight and struggle to maintain consistent temperatures. Position your greenhouse where it won’t be shadowed by trees, buildings, or other structures that could limit sun exposure.\n\nThe angle of your greenhouse roof should be calculated based on your geographical location. A general rule of thumb is to add 10-15 degrees to your latitude for the optimal roof pitch. This ensures proper snow shedding in winter and optimal light penetration year-round.\n\nConsider prevailing winds when planning your attachment point. Using your home as a windbreak can help stabilize temperatures and protect your greenhouse from harsh weather. However, ensure adequate ventilation options are included in your design to prevent overheating during warmer months. Strategic placement near existing utilities will also simplify installation and reduce costs for heating, water, and electrical connections.\n\n
 \n
\n\n\n
Structural Requirements
\n\nBefore starting construction on your attached greenhouse, it’s essential to understand and comply with local building codes and permit requirements. Most municipalities require permits for permanent structures attached to homes, and your greenhouse must meet specific structural standards for safety and durability.\n\nKey structural considerations include proper foundation work, typically requiring a concrete footer or slab that matches your home’s foundation depth. The greenhouse’s frame must be engineered to handle local snow loads and wind conditions, particularly important for year-round use. In most areas, the structure needs to withstand at least 30 pounds per square foot of snow load and wind speeds up to 90 mph.\n\nThe attachment point between your house and greenhouse requires special attention. This connection must be properly flashed and sealed to prevent water infiltration and maintain your home’s structural integrity. Many building codes require a thermal break between the two structures to meet energy efficiency standards.\n\nThe glazing material, whether glass or polycarbonate panels, must meet local safety codes for impact resistance. Double-pane materials are typically recommended for four-season use, providing better insulation and reducing heat loss. Support beams and rafters should be sized appropriately for your specific greenhouse dimensions and local climate conditions.\n\nAlways consult with a structural engineer or experienced contractor to ensure your greenhouse design meets all necessary building requirements and can withstand year-round use.\n\n\n
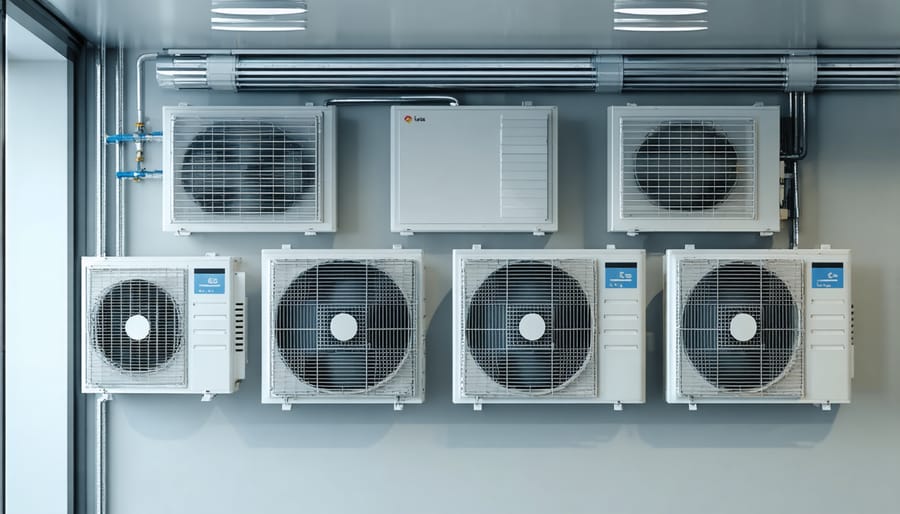
Climate Control Systems
\n\n
 \n
\n\n\n
Heating and Cooling Solutions
\n\nMaintaining optimal temperature in your attached greenhouse throughout the year requires a thoughtful combination of climate control systems and smart design choices. During winter months, the greenhouse can be heated using a combination of passive and active methods. South-facing windows maximize natural sunlight, while thermal mass elements like water barrels or stone floors store heat during the day and release it at night.\n\nFor summer cooling, installing automated vent systems helps manage excess heat. Shade cloths can reduce intense sunlight, while strategically placed fans improve air circulation. Many homeowners incorporate misting systems for both cooling and humidity control during warmer months.\n\nThe connection to your house offers unique advantages for temperature regulation. You can extend your home’s HVAC system into the greenhouse space, though it’s important to install separate temperature controls. Some gardeners use a simple fan system to draw warm air from the house during winter nights.\n\nHeat exchangers and ground-source systems are excellent long-term investments for maintaining consistent temperatures year-round. For budget-conscious solutions, consider starting with good insulation and manual vents, then gradually upgrading to automated systems as needed. Remember that proper sealing between your house and greenhouse prevents unwanted heat loss and maintains energy efficiency in both spaces.\n\n
Ventilation and Humidity Control
\n\nProper ventilation and humidity control are crucial for maintaining a healthy growing environment in your attached greenhouse throughout all four seasons. Install both passive and active ventilation systems to ensure optimal air circulation. Roof vents and side windows provide natural airflow, while automated fans can supplement air movement during still days or extreme weather conditions.\n\nTemperature-activated window openers are a smart investment, automatically adjusting ventilation based on internal conditions. Position intake vents near the bottom and exhaust vents at the highest points to create effective air circulation through the stack effect.\n\nManaging humidity is equally important to prevent plant diseases and structural issues. Install a combination of circulation fans and dehumidifiers to maintain ideal moisture levels between 50-70%. During winter months, when ventilation needs to be limited, use horizontal airflow fans to prevent cold spots and reduce condensation on walls and plants.\n\nConsider adding a moisture-sensitive controller that automatically activates ventilation when humidity levels rise too high. For additional control, install shade cloths or automatic shade systems that help regulate both temperature and humidity during intense summer heat.\n\nRemember to create a maintenance schedule for cleaning vents, checking fan operations, and monitoring humidity levels. This proactive approach helps prevent common issues like mold growth and ensures your attached greenhouse remains a productive growing space year-round.\n\n\n
Maintenance and Seasonal Preparations
\n\n
Seasonal Maintenance Checklist
\n\nKeeping your attached greenhouse thriving throughout the year requires attention to specific seasonal tasks. Here’s what you need to focus on during each season:\n\nSpring (March-May):\n- Clean and disinfect all surfaces, including glass panels and framework\n- Check and repair any winter damage to seals or structural elements\n- Test ventilation systems and clean fan filters\n- Inspect irrigation systems and replace damaged components\n- Remove winter insulation materials\n- Start seedlings and prepare growing areas\n\nSummer (June-August):\n- Clean glass panels monthly to maximize light transmission\n- Check and maintain shade cloths or screens\n- Monitor ventilation system performance daily\n- Inspect and clean gutters\n- Test automatic watering systems weekly\n- Trim any external vegetation that may shade the greenhouse\n\nFall (September-November):\n- Clean and store summer shade materials\n- Check heating system and thermostats\n- Install winter insulation materials\n- Clean and sanitize empty growing spaces\n- Inspect weather stripping around doors and vents\n- Clear gutters of fallen leaves\n\nWinter (December-February):\n- Monitor heating system performance daily\n- Clear snow from roof and exterior walls promptly\n- Check for ice buildup around vents and gutters\n- Maintain minimum temperature requirements\n- Inspect for drafts or cold spots\n- Keep pathways clear and safe\n\nRemember to maintain a maintenance log throughout the year, noting any issues that need attention. Regular inspections help prevent small problems from becoming major repairs, ensuring your attached greenhouse remains productive across all seasons.\n\n
Common Issues and Solutions
\n\nEven well-planned attached greenhouses can face several common challenges, but most have straightforward solutions. Temperature regulation often tops the list, with overheating being particularly problematic during summer months. Installing automated vent systems and shade cloths can effectively manage excess heat, while proper insulation and supplemental heating may be necessary for winter temperature maintenance.\n\nHumidity control presents another frequent challenge. High moisture levels can lead to condensation dripping onto plants and potentially damaging your home’s structure. Installing proper ventilation fans and maintaining good air circulation helps mitigate this issue. Using dehumidifiers during particularly damp periods can also prove beneficial.\n\nPest management requires vigilance in attached greenhouses. Since the structure connects to your home, any pest problems can potentially spread indoors. Regular inspection of plants, maintaining cleanliness, and using physical barriers like fine mesh screens on vents can prevent most pest issues. If problems arise, opt for organic pest control methods to keep your living space chemical-free.\n\nSome homeowners notice increased energy bills after adding an attached greenhouse. Combat this by using energy-efficient glazing materials, installing thermal curtains for nighttime use, and ensuring all seals remain tight and functional. Consider adding a thermal mass wall or water barrels to naturally regulate temperature.\n\nFoundation settling can occasionally cause gaps between the greenhouse and house structure. Regular inspection of connection points and maintaining proper drainage around the foundation can prevent most structural issues. Address any small gaps or cracks promptly to prevent heat loss and moisture problems.\n\n\nAdding a four-season greenhouse to your home is more than just a gardening upgrade – it’s an investment in your lifestyle, home value, and sustainable living practices. By creating this controlled environment that connects directly to your living space, you’ve opened up a world of possibilities for year-round growing, energy savings, and enhanced living enjoyment.\n\nThe benefits are truly remarkable: fresh herbs and vegetables throughout the year, reduced grocery bills, lower energy costs through passive solar heating, and a beautiful living space that connects you with nature regardless of the weather outside. Many homeowners also report that their attached greenhouse becomes a favorite gathering spot, combining the comfort of indoor living with the beauty of a garden sanctuary.\n\nWhether you’re an experienced gardener or just starting your growing journey, an attached greenhouse can adapt to your needs and skill level. The consistent temperature control and protection from harsh weather conditions make it easier to succeed in your gardening endeavors, while the direct access from your home ensures you’ll use and enjoy the space frequently.\n\nConsider taking the next step toward creating your own year-round growing space. With proper planning, appropriate materials, and careful consideration of your specific climate and needs, an attached greenhouse can become a cherished addition to your home that provides enjoyment and value for years to come.

